March 25th, 2025
Among the intricacies of modern manufacturing lie the fundamental aspects that make it possible to transform raw materials into a diverse arrangement of products. At the backbone of production, certain materials are propelled on a journey of polymerization and pelletization. Resulting pellets undergo a metamorphosis induced by specific additives/compounds, ultimately shaping the future of our everyday goods. Let’s look at the dynamic operations involving these components.
Raw Material Selection
A dominant factor contributing to quality product fabrication is choice of polymers. Since each one possesses distinct attributes, finding the perfect match for its related application is crucial. Whether you decide to pick polypropylene for toughness, polyethylene due to malleability or PVC for versatility, the initial selection is important. Plastics can be petroleum based, sourced from fossil fuels or biobased, derived through renewable resource.
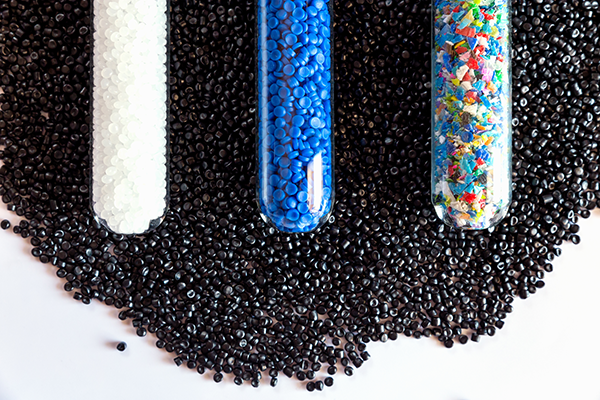

Material Reinforcement
Beyond your primary commodity, an assortment of additives might be considered to improve on desired outcome. These include stabilizers, coolants, plasticizers and other reinforcing agents, which work together to yield merchandise suitable for intended use.
- Stabilizers – Improve resistance to degradation from heat, light or chemical exposure.
- Colorants – Pigments and dyes provide aesthetic value and add visual interest.
- Plasticizers – Increase flexibility and workability, reducing overall hardness.
- Reinforcing agents – Fillers including glass fibers, carbon fibers or mineral based elements provide strength and reduce shrinkage.
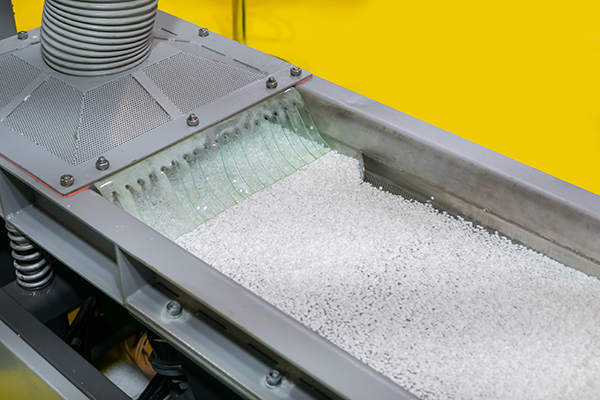
Polymerization
After selecting your desired raw composites, the polymerization stage begins. To create the basis of the plastic, individual monomers are chemically bonded to form an extensive chain to produce polymers. In addition to establishing chains, this step influences molecular weight and structure which later reflects on the plastic’s physical characteristics. The by-product is then processed into tiny, uniform pellets that are fed through machines for additional manufacturing procedures.

Molding Process
Following polymerization, various methods of fabrication are used to fashion polymers into tangible objects.
- Extrusion – Forces molten plastic through a die to create long continuous shapes.
- Injection Molding – Fills a hollow mold cavity to mimic specific shapes or designs.
- Blow Molding – Creates hollow objects by blowing air into the molten plastic to expand the mold.
Quality Control
Once the plastic items are completed, incremental changes to solidify shape, finish and functionality could be required. These alterations may include trimming, sanding, painting or coating. Testing is done to determine dimensional accuracy, performance and overall structural integrity. This phase is imperative in certifying specifications are met and the product meets control standards before repeating the process.
The journey from raw material to finished plastic product is a complex and multi-faceted progression that entails careful selection of polymers, reinforcement with additives, polymerization and molding. Through extrusion, injection molding and blow molding, raw materials transform into the versatile and indispensable products that we use in our daily lives.